I. The Transformation of American Law
A. Emergence of the private corporation: Dartmouth College v. Woodward (1819)
B. Contract law: Increasing "freedom of contract" and protections for private profits
1. Fall of "consideration" and the rise of the "will theory" of contracts and the "caveat emptor" doctrine.
2. Fletcher v. Peck (1810): A contract is a contract, even if fraudulent.C. Destruction of impediments to economic development: decline of "riparian" and other customary property rights
D. Labor unions as conspiracies: The Philadelphia Cordwainers' Case (1806)
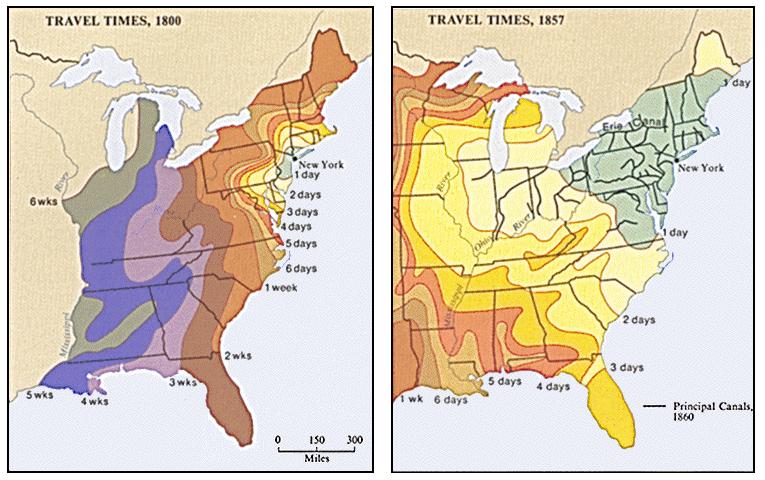
II. Before the Railroads: The Early Transportation Revolution

A. Main issues: topography, access to the interior, transportation costs (freight rates) and times.
B. The movement for improved roads
1. "Common" roads: cleared paths built and maintained by locals.
2. The problem of through-routes
3. Indian wars and road-building
4. The Turnpike Era, 1794-1830
5. Bridges: more successful than turnpikes
6. Plank roadsC. The Erie Canal: Gateway for the Market Revolution
1. Political background: Madison and the "Bonus" bill veto, 1817
2. Clinton and New York strike out on their own, redirect development efforts to the state level.
3. The Erie Canal and the rise of New York City.D. The Canal Boom
1. Massive (quasi-public) expenditures in Northeast and Midwest: chartered corporations, state bonds, land grants.
2. Limits of the "Revolution": Projects successful only where there were decent routes, existing markets or obvious resources.
3. "Anthracite" canals, connections between major cities and rivers succeeded (Delaware & Raritan, Ohio), most others (Pennsylvania Main Line, Indiana) failed. Some served public better than investors.
4. Political aspects: many failed due to politically-inspired overexpansion.E. Steamboats: Most important form of transportation, 1820-1850
1. Commercial navigation began with Fulton-Livingston group, who in 1807 secured steamboat monopoly from NY legislature.
2. Dramatic expansion of eastern steamboat navigation after Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) broke the monopoly, on interstate level.
3. Steamboats most important on western rivers.
4. First area of federal regulation.F. Rivers and the lack of a Transportation Revolution in the South.